Development of a Novel System for Building Artificial Enantioselective Catalysts
Abstract
Enzyme catalysis is the most efficient strategy for preparation of enantiopure products by now. Unfortunately, many reactions important for industrial applications are missing from nature’s toolbox(1). Most of those reactions (e.g. hydrogenation, hydroformylation) are catalysed by 4d/5d transition metal ions. Incorporation of these transition metals into a protein host via a ligand leads to a novel class of hybrid catalysts, so called artificial metalloenzymes(2). However, creation of synthetic activity from scratch within an existing protein scaffold still remains a challenging task(3).
The RNase S system provides an ideal framework to incorporate nonnatural catalytic centres into a protein environment using peptide protein complementation (RNase S = S-protein + S-peptide). The basic catalytic activity is provided by the metal-organic centre whereas the protein environment ensures enantio- and regioselectivity. Based on the structure of RNase S we intend to design a system for creation of various enantioselective catalysts.
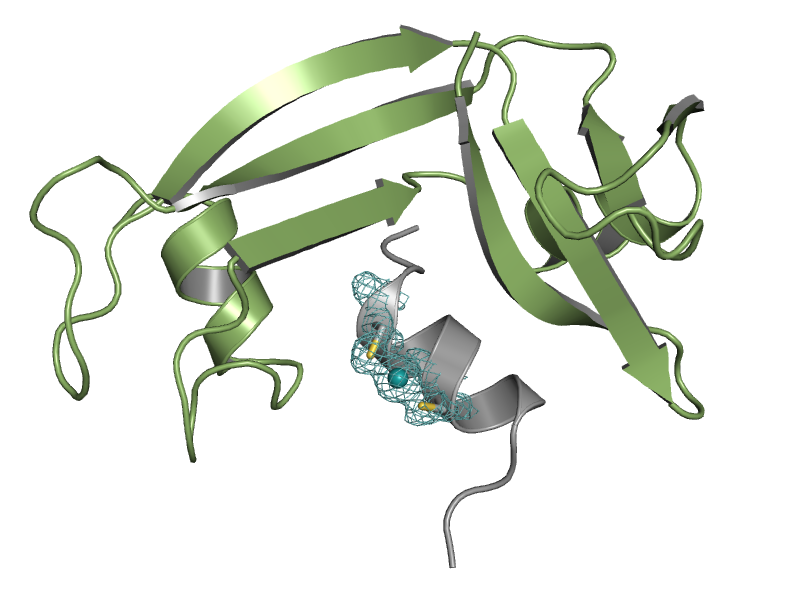
So far, we produced crystals of an artificial metalloprotein comprising a RNase S variant with cysteines used as metal binding site. The X-ray structure revealed the formation of a stable [Cys2Hg] centre while the protein fold is not alteres (see figure). The Crystal structure guided us for building a model of RNase S with a rhodium ion complexed by two artificial diphenylphosphine amino acids. Currently, we are working on the first RNase S variants for establishing hybrid catalysts.
References
(1) Jing, Okrasa & Kazlauskas, Chem. Eur. J., 2009, 15, 1370-1376
(2) Wilson & Whitesides, J. Am. Chem. Soc., 1978, 100, 306
(3) Creus & Ward, Org. Biomol. Chem., 2007, 5, 1835-1844

