Combined use of Crystallography and CryoEM in the structure determination of giant hemocyanins
Abstract
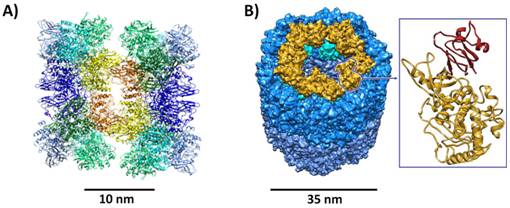
Hemocyanins are extremely large protein complexes (MR up to 8.0 MDa) which cooperatively bind oxygen at their type 3 copper active sites. Structural analysis of hemocyanins is a challenge due to their very large size. However, in recent years advances have been made by a combination of cryoEM reconstruction and X-ray crystallography [1-4]. Here we present our recent results such as the 6.5 Å X-ray crystallographic structure of scorpion hemocyanin (1.8 MDa, Fig. 1A), which in connection with its respective cryoEM structures gives a clue for structural changes associated with activation of its intrinsic phenoloxidase activity [1]. Furthermore results on the crystallographic analysis of the native Octopus hemocyanin decamer (3.6 MDa) and the structure of a single functional unit (KLH1-h, Fig. 1B) of Keyhole limpet hemocyanin, which is of medical importance in cancer treatment, will be presented [2-4].
Acknowledgements: Financed by GK 1043 (DFG), the "Computational Science Mainz" (CSM) and "Research Center Immunology" (FZI) of the Gutenberg University. We thank T. Barends & I. Schlichting (MPI Heidelberg) for providing access to X-ray sources, Y. Cong & W. Chiu (NCMI, Houston) for CryoEM reconstructions and G. Schroeder (Forschungszentrum Jülich) for low resolution refinement.
References
[1] Cong, Y., et al. (2009). Structure 17:749-758
[2] Gatsogannis, C., et al. (2009). J. Mol. Biol. 385:963-983
[3] Jaenicke, E., et al (2011). IUBMB Life 63:183-187
[4] Jaenicke, E., et al (2010). Biochem. J. 426:373-378

