Screening of a naïve VHH antibody library from non-immunized Lama glama using phage and yeast display and isolation of binders against various targets
Abstract
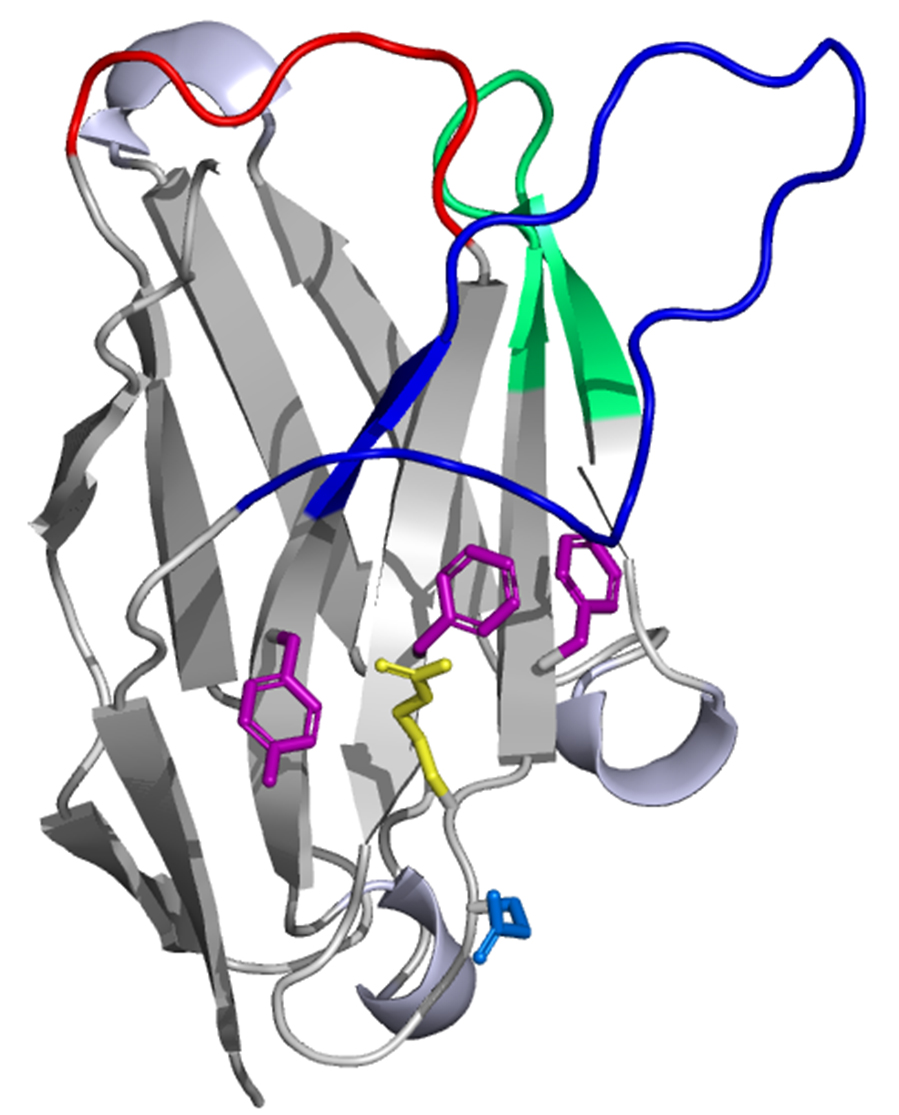
Antibodies are powerful tools in applied biotechnology and medical research. To gain access to antibodies with high affinity, selectivity, and stability large synthetic and naïve libraries have been generated that were screened by in vivo and in vitro methods.[1,2] An alternative to scFvs, which are one of the most commonly used scaffolds, are the variable domains of heavy-chain antibodies (HCAbs) from Camelidae. HCAbs are antibody molecules that are devoid of light-chains and possess a single variable antigen-binding domain designated as VHH (variable domain of the heavy chain of a heavy-chain antibody) (Fig.1). HCAbs are often more stable than conventional antibodies, are of small size, have higher solubility, higher expression yields in heterologous expression systems and are able to bind to alternative epitopes, e.g. they are capable of blocking the active site of enzymes. [3] We have established two full naïve VHH antibody libraries from non-immunized llamas (Lama glama) in phage and yeast with a functional diversity of 3 x 109 and 5 x 108 individual variants, respectively. Among others, binders against several targets including green fluorescent protein (GFP), thioredoxin, human C4 binding protein and also the cancer targets matriptase and cadherin have been isolated by high throughput yeast and phage display screening. We show that VHHs can be isolated, produced in E. coli and used for various applications obviating the need for animal immunization.
References
[1] Chao et al. (2006) Nat Protoc 1(2):755-768.
[2] Monegal et al. (2009) PEDS 22(4):273-280.
[3] Muyldermans et al. (2001) Trends Biochem Sci.
26(4):230-235.

