Acetylation-Reporters for Residue-Specific Histone Deacetylase and Acetyl-Transferase Profiling in Real Time
Abstract
Reversible lysine acetylation of histone proteins is a common post-translational protein modification. Histones package DNA into chromatin and acetylation of their ‘tail’ regions establishes, in part, the ‘epigenetic chromatin code’ by promoting permissive (acetylated) or repressive (deacetylated) states of gene expression [1]. Histone acetylation is catalyzed by a set of enzymes collectively referred to as histone acetyl-transferases, or HATs. Histone deacetylases, or HDACs, perform the ‘opposite’ reaction and selectively remove acetyl moieties from modified lysine residues. Because of their roles as general transcriptional modulators, HATs and HDACs have gained considerable attention and the investigation of their catalytic properties is a current topic in biomedical sciences [2].
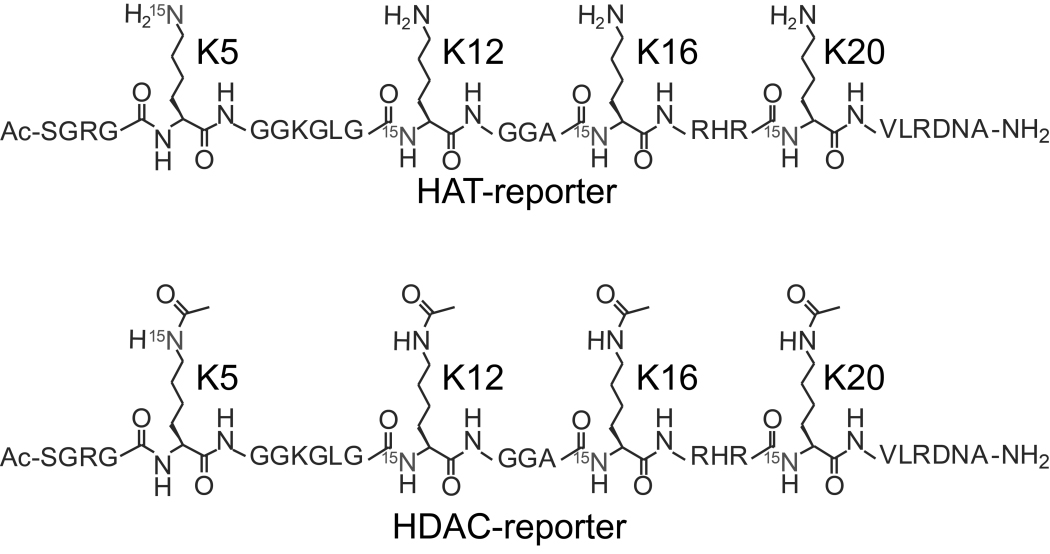
This talk will introduce a new method for monitoring the activity of HATs and HDACs, which is based on characteristic NMR-effects acetylated lysine residues display in 1H/15N correlation experiments [3,4]. We describe the chemical synthesis of isotope-labeled deacetylation and acetylation reporters for simultaneous readouts of multiple deacetylation and acetylation reactions at different histone H4 sites. The site preferences of two prototypic histone deacetylases (Sir2.1 and HDAC8), and two acetyl-transferases (HAT1 and p300/CBP), were studied in competition reactions. We identify a previously ill-defined acetylation site, lysine 20 of histone H4, as a preferred target of three of theses enzymes. In situ analyses of endogenous deacetylation reactions at H4 sites in HeLa nuclear extracts point to abundant HDAC activities in human cellular environments [5].
References
1. Schwarzer D., J. Pept. Sci. 2010, 16, 530-537.
2. Gallinari P., Di Marco S., Jones P., Pallaoro M., Steinkuhler, C., Cell Res. 2007, 17, 195-211.
3. Liokatis S., Dose A., Schwarzer D., Selenko, P., J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2010, 132, 14704-14705.
4. Smet-Nocca C., Wieruszeski J. M., Melnyk O., Benecke A., J. Pept. Sci., 2010, 16, 414-423.
5. Dose A., Liokatis S., Theillet X.-F., Selenko, P., Schwarzer D., ACS Chem Biol. 2011, 6: 419-424.

